
Keywords:Arctic Governance, Polar Code, UNCLOS, Sustainable Development Goals, Arctic Treaties, Indigenous Rights, Arctic Council, India’s Arctic Programme, Climate Change, Arctic Research
Governance Mechanisms in the Arctic
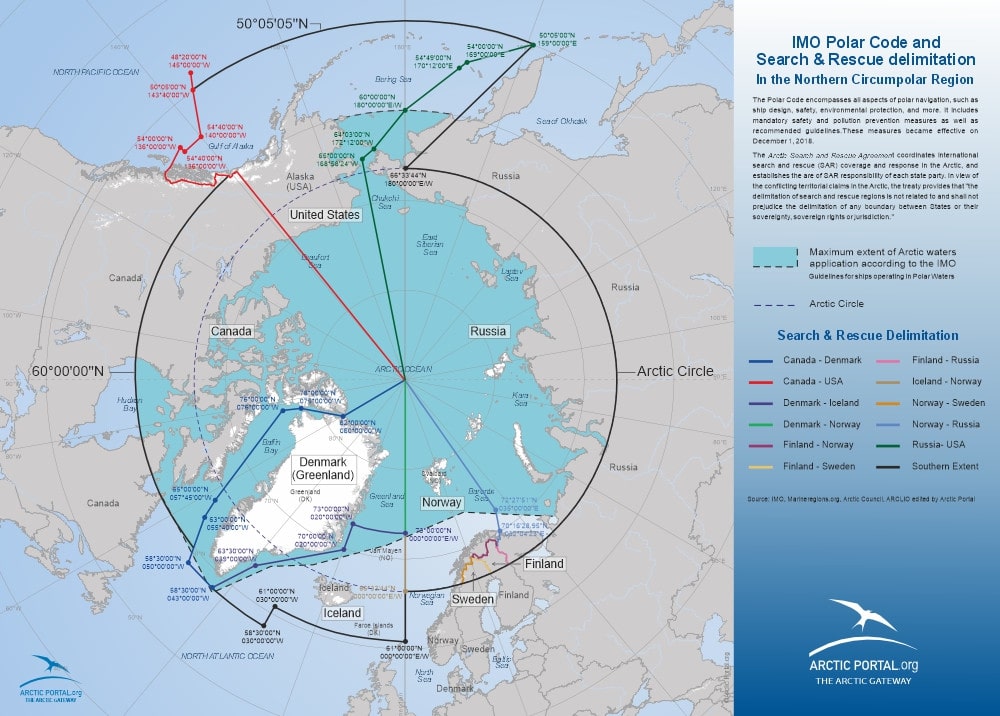
The Arctic region is governed through a combination of sovereign jurisdictions, international treaties, regional agreements, and customary laws that guide both state and non-state actors. Unlike other regions, the Arctic does not have a single overarching treaty but instead relies on bilateral and multilateral frameworks to address environ mental, economic, and security issues.
Key Governance Mechanisms
Sovereign Jurisdiction: The Arctic is governed by the eight Arctic states—Canada, Denmark (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Russia, and the United States—which exercise national sovereignty over their respective territories.
International Treaties and Conventions:
- UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea) – Defines maritime boundaries, resource rights, and territorial claims in the Arctic.
- UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) – Guides sustainable economic development and environmental protection in Arctic policies.
- International Environmental Treaties – Includes climate change agreements, biodiversity protection, and pollution control measures.
- Oil and Gas Liability Regimes – Establish liability frameworks for oil exploration and drilling activities to prevent environmental damage.
- International Human Rights Instruments – Protects the rights of Indigenous Arctic communities and ensures their participation in governance.
Regional Frameworks and Organizations
- Svalbard Treaty (1920) – Governs territorial rights and resource access in the Svalbard archipelago.
- 1973 Agreement on the Conservation of Polar Bears – Ensures polar bear conservation efforts across Arctic nations.
- Arctic Council – The leading intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation on environmental protection and sustainable development.
- Barents Euro-Arctic Council (BEAC) – Enhances regional economic cooperation in the Arctic.
- Nordic Defence Cooperation (NORDEFCO) – Focuses on defense collaboration among Nordic countries.
- Arctic Coast Guard Forum (ACGF) – Strengthens maritime safety and security cooperation.
- Arctic Economic Council (AEC) – Facilitates business and trade in the Arctic.
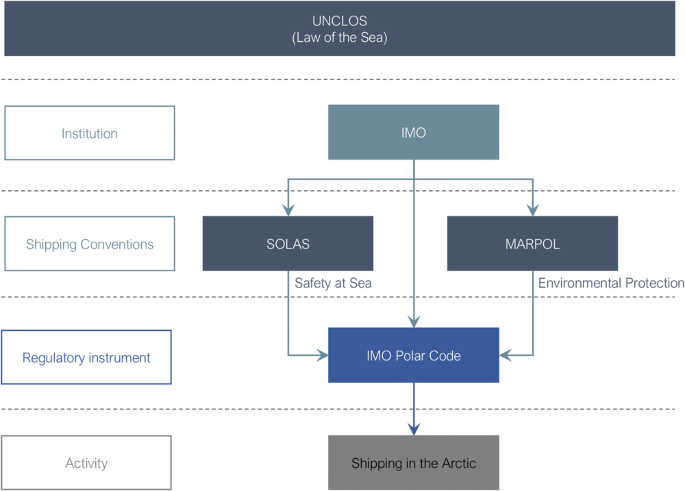
India, though a non-Arctic nation, has been actively contributing to Arctic research through its Arctic Programme, which aims to enhance scientific understanding of climate change and its impacts.
Key Objectives of India’s Arctic Programme
- Enhancing knowledge on climate change adaptation and mitigation.
- Conducting atmospheric, biological, marine, earth sciences, and glaciological studies.
- Strengthening scientific cooperation with Arctic states and international organizations.
India’s Arctic Research Areas
Atmospheric Research
- Studies on aerosols, precursor gases, and their optical properties.
- Research on space weather effects on the auroral ionosphere.
Biological and Marine Studies
- Investigation of sea-ice microbial communities.
- Research on marine phytoplankton, ecological parameters, and ocean chemistry.
Earth Sciences and Glaciology
- Observations on carbon monoxide production in snowpacks and its diurnal variability.
Conclusion
The Arctic is governed through a complex network of treaties, organizations, and national policies, with the Polar Code being the primary legal instrument for regulating maritime activities. While Arctic governance remains primarily in the hands of the eight Arctic states, non-Arctic nations like India play an increasing role in Arctic research, contributing to climate studies and international scientific cooperation. As climate change accelerates, global collaboration in the Arctic will become increasingly crucial for sustainable development and environmental conservation.
Tags:#ArcticGovernance #PolarCode #UNCLOS #ClimateChange #ArcticCouncil #IndiaInArctic #EnvironmentalProtection #ScientificResearch
For more updates on environmental regulations, public health policies, and developments in India's governance, follow Kanishk Social Media for comprehensive and timely coverage of critical issues. If you found this article helpful, share it with others interested in India’s environmental efforts and policy innovations.










0 Comments